The National Museum of Egyptian Civilization includes a group of scientific research laboratories specialized in accurate analyses, which serve work in the archaeological field as well as scientific research in all different fields. It includes the following laboratories:

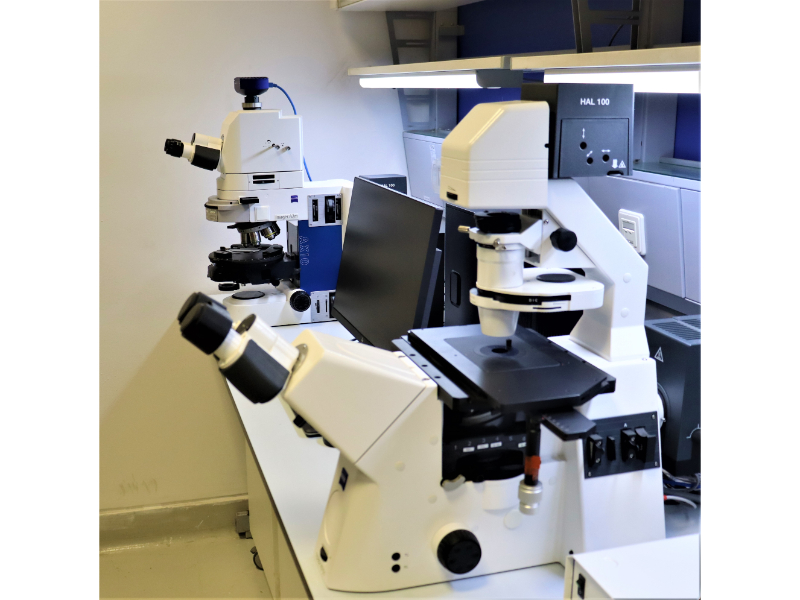
Our Microscopy Unit offers a comprehensive service to researchers and provides technical and methodological support in the development of projects that require these techniques like biology, geology, engineering, medicine and archaeology.
It contains: Polarized microscope, Inverted metallurgy microscope, Inverted fluorescence microscope, stereomicroscope, and Upright fluorescence microscope.

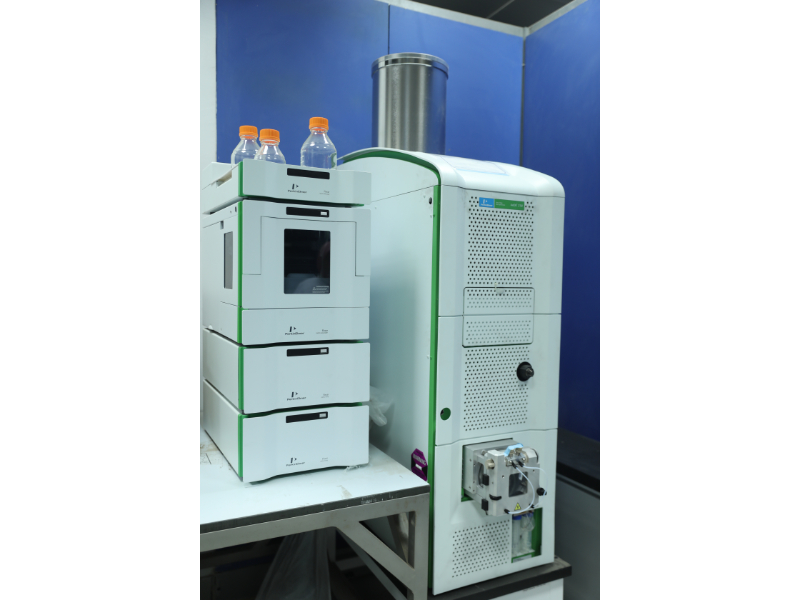
The chromatography unit separates, identifies, and Quantification of organic matters present in a sample. Therefore used to analyze a wide range of organic materials, including lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, resins, waxes, dyes, plant extracts, animal fats and other biomolecules. The unit contains two major devices (UPLC-ToF) and (GC-MS-HS).

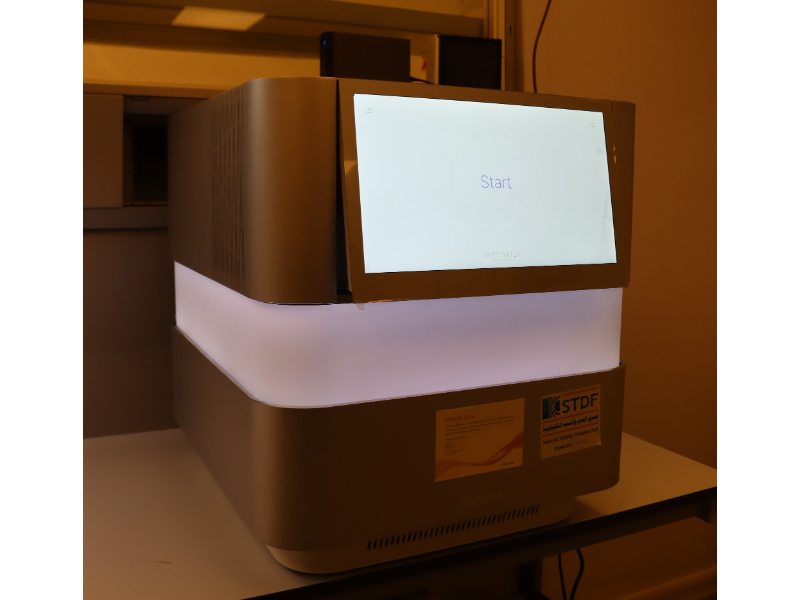
It is the first reference laboratory in Africa to study ancient human, animal and plant DNA. The laboratory aims to establish advanced methods for extracting and analyzing various archaeological biological samples in order to establish them in the future as a routine analysis. The lab also studies human kinship, in addition to studying diseases in the environment in ancient Egypt. The laboratory contains many advanced equipment specialized in DNA analysis.

The radiocarbon unit is a unique unit because of its great importance, through which it is possible to date organic archaeological materials such as: papyrus, manuscripts, wood, pottery and some other materials via radioactive carbon dating. It can also in the distinction between original and counterfeit art pieces
The laboratory isolates and defines different types of microorganisms from all different types of samples. The laboratory also studies the best possible methods for treatment and elimination of microbial contamination in the environment. The laboratory also allows researchers and scholars to conduct some tests related to the study of microbiology

The laboratory analyzes organic matters, identifies protein and what it contains of amino acids and dyes, and measures the quality of various products. It is also used in analyzes of biomedical research such as the pharmaceutical industry and academic scientific research. The laboratory contains two main devices:
the Ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometer and the fluorescence spectrophotometer

can be used to measure the weight of the sample at different temperatures and determine the loss in weight with the increase in temperature in addition to studying the thermal stability of pharmaceuticals and a better definition of bound and free water in pharmaceuticals and the heat flow in different materials and determining the degree of glass transition, heat capacity and melting point as well The degree of purity of the substance. The laboratory contains some devices: (TGA), (DMA),
( DSC), (TGA- FT-IR microscopy).

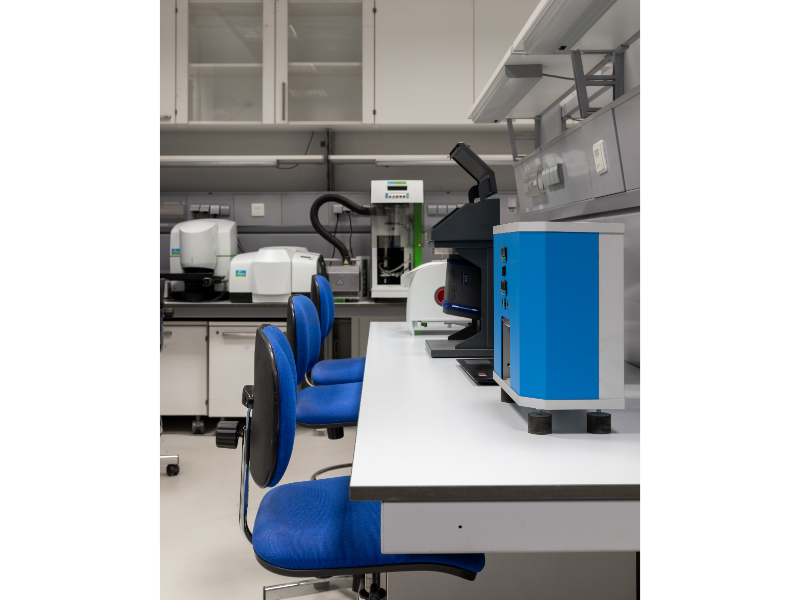
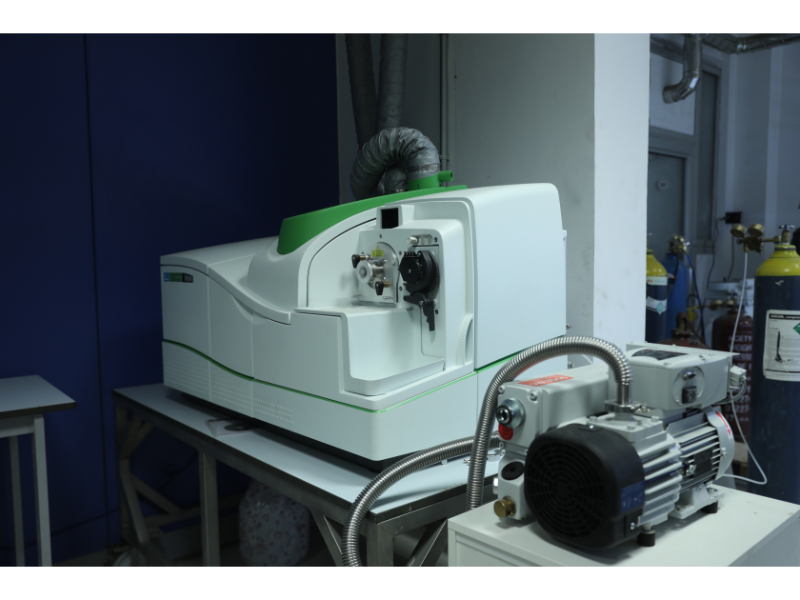
This laboratory Specializes in analyzing most of the elements of the periodic table, especially heavy metals, rare elements and isotopes. The process includes identifying and quantifying elements at very low concentration levels, up to one part per trillion (ppt) of the sample. Elemental analysis is used in many fields, such as the food industry, drinking water analysis, and in the fields of pharmacy and biomedicine. Isotope analysis can also be used to find out the ratios of isotopes that are used in the geological dating of rocks. The laboratory contains two main devices: Atomic Absorption Spectrometer and (LA-ICP-MS)

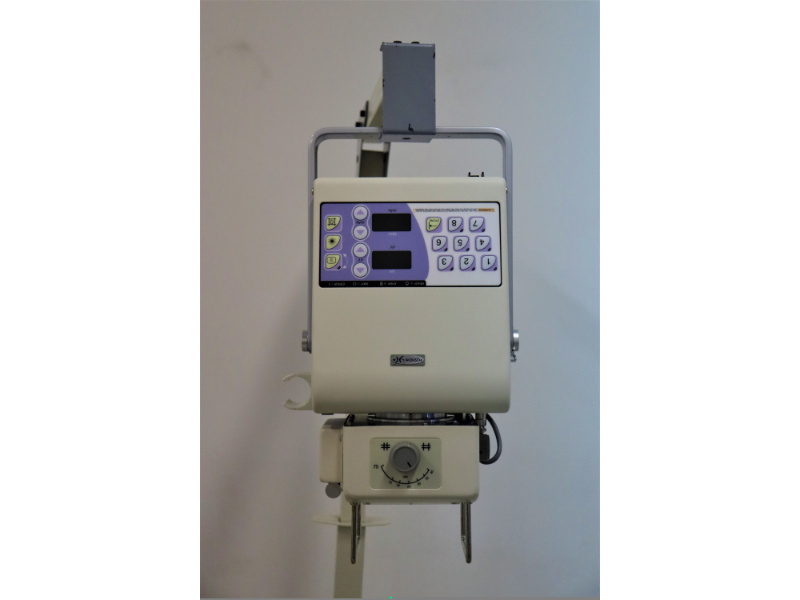
The X-ray imaging device is used to study the various mummified by imaging the bones, locating the fractures in them, and identifying the solid objects inside the body. The device can also be used to differentiate between the real and fake paintings.

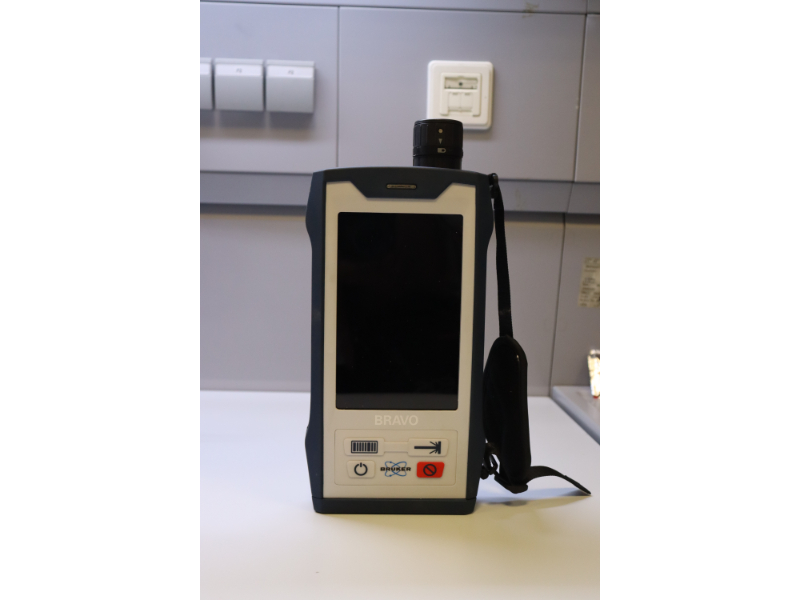
It is a non-destructive unit that analyze chemical, mineralogical, gemological and other materials and is extraordinary useful in the field of archaeology, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, geology and mineralogy, carbon materials, semiconductors, bio-cells, bone structure, drug cell interactions, DNA/RNA analysis, and so on.

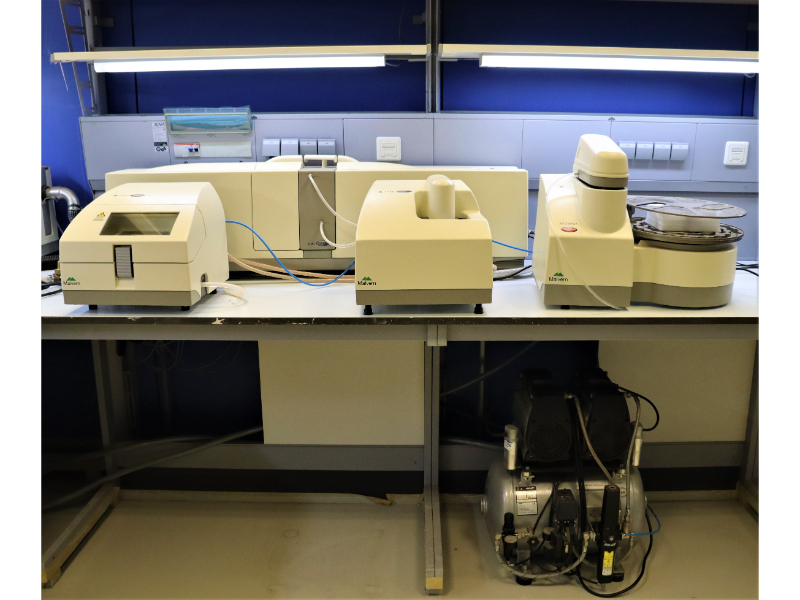
The Mastersizer 2000 is a practical, reliable and important solution for measuring the particle size and particle size distribution of materials. It is one of the devices that meets the daily industry needs for particle sizing.

A unit specialized in sterilizing antiquities and art pieces by replacing oxygen gas with nitrogen gas, which is toxic to most insects that may be contained in the artifact, taking into account that nitrogen gas has no effect on artifacts, and therefore it is considered one of the methods of insect control that is characterized by its low price and secure it to the exhibits.

The laboratory studies archaeological plants resulting from various excavations and determines the type of plant varieties for the purpose of studying and archaeological documentation of different plants and re-imagining the plant environment in the past. It can also host scholars to study samples for their research projects.

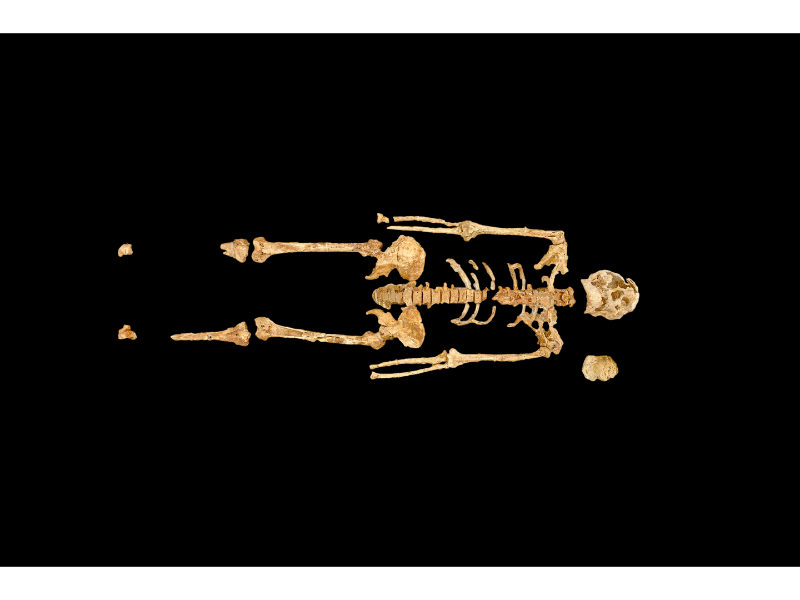
Studying human remains is the focus at the National museum of Egyptian civilization Bioarchaeology Laboratory. A deeper scientific understanding of past life and how people interacted with their environments is gained using physical anthropology to identify human origins, ages, and mortality rates in ancient cultures. The lab is also concerned with studying the origins and spread of diseases that have plagued people for centuries. Doing so advances our understanding of disease and health in earlier populations and societies, and provides solutions to some medical problems that have been affecting us in present day regarding the emergence and evolution of diseases. The laboratory uses non-destructive scientific methods to study ancient humans, such as radiography, biometrics, biochemical analyses, and microscopic analyses.
It is a unique unit of its kind in Egypt, where the unit moves to the site to carry out various analyzes such as detect elements and their concentration in any sample, determining the origin or age of art holdings, soil analysis, dye analysis, determining the proportions of heavy metals in materials, as well as the final test of industrial products and Photographing mummified.
The unit includes: Raman spectrometer, X-ray device, X-ray fluorescence device, and infrared spectrometer

It is a laboratory that contains many auxiliary devices that the researcher may need in some tests related to his scientific project, such as a viscosity measuring device, a rotary separator, a lyophilizer, a water distillation device, a heat sterilizer, a water bath, a centrifuge, a mill, etc.

It is a reference unit for preserving biological samples from different organisms as one of the main foundations in life science research and in preserving the genetic origins of various organisms. Also it will save samples of extinction-prone organisms (such as; some types of wild, rare plants and animals, or microbes with unique characteristics). The bank will store samples using an integrated classification system and thorough scientific documentation

For more information contact us at scientific.labs@nmec.gov.eg
